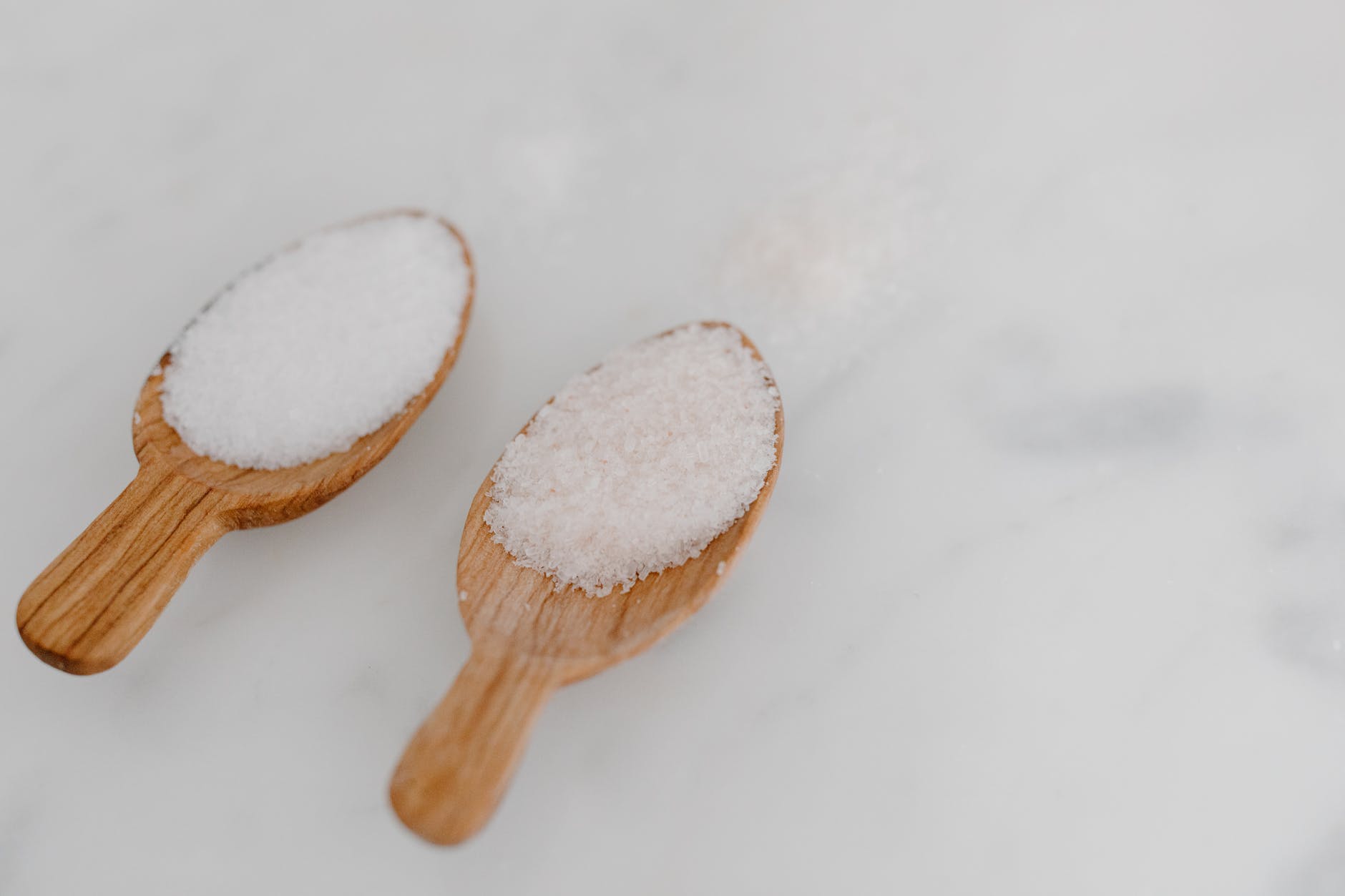
Stock up on Salt and Sugar: Sugar and salt are among the most common household substances and have been widely used since the dawn of time. There is no kitchen in which you cannot find these two substances with a very similar appearance but with a completely different flavor!
In addition to being essential for our life, these two foods are excellent allies to preserve and disinfect: in this article I’ll briefly explain why.
Stock up on Salt and Sugar: How long do salt and sugar last?
As you may already know after reading Food that never expires: 7 products for your food supply , salt and sugar are non-perishable substances , as long as they are stored correctly. The general rule is to keep them in airtight bags or containers away from moisture.
They are two hygroscopic substances, that is, they suck and retain humidity in the air, therefore to keep them long-term it is best to keep them in a cool and dry place, possibly in vacuum -sealed or bags . And by long term, I mean even centuries.
Survival uses of salt
Our body needs salt to function. People may live without sugar for their entire lives, but salt is another story altogether!
Unlike sugar , a refined food, salt is an essential mineral for both humans and animal life in general. While our bodies can make their own sugar from various carbohydrate-rich foods – such as fruits and grains – salt (NaCl, Sodium Chloride), is an essential mineral, readily available in nature in its natural crystalline form, also called rock salt.
Although doctors, scientists and nutritionists remind us to limit the consumption of salt, this does not mean that we can live without it, on the contrary. As reported on the ISS website;
The salt provides sodium and chlorine, two fundamental elements in regulating the body’s acid-base balance […] and the water balance. Sodium, in particular, has very important functions by regulating the amount of water present in the blood and between tissue cells. In addition, it affects muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission.
Higher Institute of Health
The limitation of the use of salt in food is mainly due to what is defined as “occult salt”, that is all that salt used in the preparation of ready-made or semi-finished foods. We think of sausages, cheeses, snacks or ready-made delicatessen products.
Also according to the ISS, the amount of sodium needed by our body is 2g per day, equivalent to 5g of salt, preferably iodized . However, things can change dramatically, especially in an SHTF scenario .

1. Salt to preserve food
Let’s start with the most obvious one: food preservation. Salt dehydrates, therefore it is perfect for a “primitive” preservation of food , especially if we are talking about meat or game, even without the aid of refrigeration systems.
Two main methods can be used to preserve with salt: dry or brine salting. In the first case, the food is completely covered with salt, preferably inside a glass or wooden container. This technique absorbs the humidity inside the container and dehydrates the surface layer of the food, delaying the oxidation processes. Before consumption, the food must be washed thoroughly to remove the surface salt layer.
Little trick: it is better to use coarse salt as the fine salt penetrates too quickly inside the food, creating a sort of barrier that will not allow a deep dehydration that will nullify the conservation.
The second method, brine, is completely analogous even if it uses water as a carrier. In fact, a solution of water and salt is prepared, with different intensities, in which the product will be immersed. We speak of weak brine if the percentage of salt per liter is less than 10%, medium brine if the content fluctuates from 10% to 25%, while strong brine if higher than 25%.
Pink, black, green and blue salt: does it make sense to buy them? Do they last longer?
Spoiler alert: no. Pink Himalayan salt is a salt made colored by iron oxide. As the good Prof. Bressanini says: “you are eating salt with rust”. These types of salt are “dirty” or not very pure. Therefore, the white salt you find on the market is refined and with a high purity. In a nutshell, you couldn’t wish for anything better
2. Salt to disinfect
Linking to the previous point, a weak, very weak brine can be used as a disinfectant for superficial wounds. In this case, the “medical brine” takes the name of physiological solution
The composition of a physiological solution imposes sterile, distilled water and 1% sodium chloride. If necessary, to make a makeshift physiological solution, simply heat clean, drinkable water (heat, do not boil) and add 10 grams of salt , possibly non-iodized, for each liter.
This makeshift saline solution is excellent for rinsing and cleaning superficial wounds of foreign bodies, microbes and other foreign bodies without damaging the tissues. In fact, the physiological solution is called isotonic, that is, it does not subtract or add liquids to the wound itself. I recommend, avoid applying the salt directly on the wound, as long as you do not name the saints on the calendar one by one.
Survival uses for sugar

1. Sugar to preserve
Just like salt, sugar can be used as a food preservative and works the same way: thanks to its osmotic effect, sugar dehydrates bacteria by killing them and preserving food.
Sugar increases the acidity of foods, a very useful aspect especially in the making of preserves. In fact, a percentage higher than 25% protects against the development of Botox in homemade preserves . This is why jams and marmalades are rich in sugar.
2. Sugar to disinfect
In a completely similar way to salt, thanks to its osmotic action, even sugar can be used in the preparation of a makeshift disinfectant solution. Perhaps, it is good to avoid using it in the treatment of canker sores or wounds of the oral cavity, only to then have to treat some dental caries.
In conclusion, if you were wondering “better to stock up on salt or sugar?”, The immediate answer is both, although salt should probably be a priority, as our body cannot produce it.
I hope this article was of interest to you. Write in the comments which alternative or household uses of salt you know.