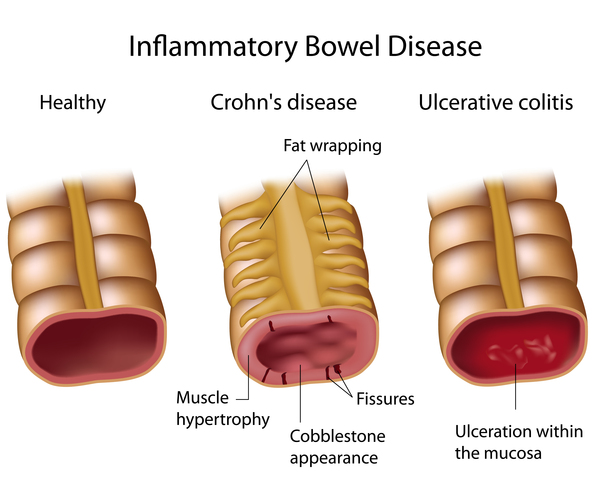
Patients with this type of pathology, once diagnosed, are linked to the Digestive Unit and are referred to the specific Inflammatory Bowel Disease pathology consultations where they can start treatment and monitor their outbreaks and their periods of remission between outbreaks. .
From primary care it is important to know the treatments of these patients and the usual symptoms of outbreaks as well as the possible adverse effects or complications of the treatments and thus achieve adequate monitoring of the patients by the two teams.
treatment lines
The treatment of Crohn’s disease has been advancing in recent decades, adding several lines of treatment.
The first treatments consisted of drugs that were more limited in their action and with potential side effects, such as oral or rectal Mesalazine (5-ASA), also systemic and topical corticosteroids, antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, metronidazole), and later immunosuppressants ( Thiopurines, Methotrexate).
Now, biological treatments
Recently, biological treatments have become the protagonists for the control of this pathology, which we must not forget that it is a chronic pathology, for which the objective is the stability of the patient throughout his life and the limitation of the implicit complications in this pathology.
The function of biological treatments is to produce an immunosuppressive effect at a high power and it is very effective both for the prevention of outbreaks and for controlling them.
What should be taken into account
Since its use, it is considered a better control and maintenance of patients with Crohn’s disease. The characteristic that makes them so effective also creates the need to take precautions before starting their use at the beginning and throughout the treatment.
- It is important to remember that it is necessary to make a first complete assessment of the patient at the start of treatment with a biological agent. A series of tests are carried out aimed at the immunosuppressive effect produced by these drugs, and which therefore can reactivate infections that remain latent, so it is very important to screen for the most frequent infectious diseases that can remain dormant for a long time. ( HBV , HCV , HIV and TB ).hep
- A review of the patient’s vaccination status should also be made and completed if necessary .
- Once treatment has started , active monitoring of patients is carried out , for example, in most of those who take biological treatments, treatment with antivirals is indicated if they have a coronavirus infection to prevent progression, since being immunosuppressed the risk may be higher than in the general population.
- There are three families of biological drugs approved for IBD: Anti-TNFα monoclonal antibodies (Infliximab, Adalimumab, Golimumab and certolizumab), Anti-integrin monoclonal antibodies (Vedoli-zumab) and Anti-inter-leukin monoclonal antibodies (Ustekinumab). The treatment decision will be made by the IBD team.
Thanks to research, improvements and new treatments are expected in the coming years for this type of pathology.
What you should know…
- Recently, biological treatments have become the protagonists for the control of Crohn’s disease.
- The function of biological treatments is to produce an immunosuppressive effect at a high power and is very effective both for the prevention of outbreaks and for their control.
- The characteristic that makes them so effective also creates the need to take precautions before starting their use at the beginning and throughout the treatment.